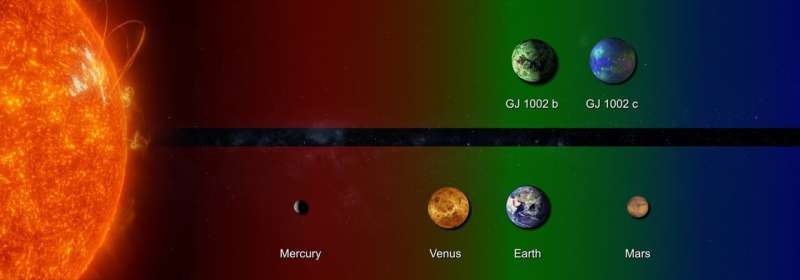
A global scientific group led by researchers on the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) has found the presence of two planets with Earth-like plenty in orbit across the star GJ 1002, a red dwarf not removed from the solar system. Each planets are within the habitability zone of the star
“Nature appears bent on displaying us that Earth-like planets are quite common. With these two we now know 7 in planetary systems fairly close to to the sun,” explains Alejandro Suárez Mascareño, an IAC researcher, who’s the primary creator of the research accepted for publication in Astronomy & Astrophysics.
The newly found planets orbit the star GJ 1002, which is at a distance of lower than 16 light years from the solar system. Each of them have plenty just like that of the Earth, and they’re within the habitability zone of their star. GJ 1002b, the internal of the 2, takes little greater than 10 days to finish an orbit across the star, whereas GJ 1002c wants a bit over 21 days.
“GJ 1002 is a red dwarf star, with barely one eighth the mass of the sun. It’s fairly a cool, faint star. Which means its habitability zone could be very near the star,” explains Vera María Passegger, a co-author of the article and an IAC researcher.
The proximity of the star to our solar system implies that the 2 planets, particularly GJ 1002c, are wonderful candidates for the characterization of their atmospheres based mostly both on their mirrored gentle, or on their thermal emission.
“The longer term ANDES spectrograph for the ELT telescope at ESO by which the IAC is taking part, might research the presence of oxygen within the ambiance of GJ 1002c,” notes Jonay I. González Hernández, an IAC researcher who’s a co-author of the article. As well as, each planets fulfill the traits wanted for them to be goals for the long run LIFE mission, which is presently in a research phase.
The invention was made throughout a collaboration between the consortia of the 2 devices ESPRESSO and CARMENES. GJ 1002 was noticed by CARMENES between 2017 and 2019, and by ESPRESSO between 2019 and 2021.
“Due to its low temperature the visible light from GJ 1002 is simply too faint to measure its variations in velocity with nearly all of spectrographs,” says says Ignasi Ribas, researcher on the Institute of Area Sciences (ICE-CSIC) and director of the Institut d’Estudis Espacials de Catalunya (IEEC).
CARMENES has a sensitivity over a variety of close to infrared wavelengths which is superior to these of different spectrographs aimed toward detecting variations within the velocities of stars, and this allowed it to check GJ 1002, from the three.5m telescope at Calar Alto observatory.
The mixture of ESPRESSO, and the sunshine gathering energy of the VLT 8m telescopes at ESO allowed measurements to be made with an accuracy of solely 30 cm/sec, not attainable with every other instrument on this planet.
“Both of the 2 teams would have had many difficulties if that they had tackled this work independently. Collectively now we have been capable of get a lot additional than we’d have executed performing independently,” states Suárez Mascareño.
Extra data:
A. Suárez Mascareño et al, Two temperate Earth-mass planets orbiting the close by star GJ 1002, Astronomy & Astrophysics (2022). DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/202244991
Supplied by
Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias
Quotation:
Astronomers uncover two probably liveable exo-Earths round a star close to the sun (2022, December 15)
retrieved 15 December 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-12-astronomers-potentially-habitable-exo-earths-star.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.





