On the morning of Saturday, Nov. 5, a world crew of planetary scientists awoke with nice delight to the primary Webb pictures of Saturn’s largest moon, Titan. Right here, Principal Investigator Conor Nixon and others on the Assured Time Statement (GTO) program 1251 crew utilizing Webb to research Titan’s environment and local weather describe their preliminary reactions to seeing the info.
“Titan is the one moon within the solar system with a dense atmosphere, and it’s also the one planetary physique aside from Earth that at present has rivers, lakes, and seas. In contrast to Earth, nonetheless, the liquid on Titan’s floor consists of hydrocarbons together with methane and ethane, not water. Its environment is crammed with thick haze that obscures seen gentle reflecting off the floor.
“We had waited for years to make use of Webb’s infrared imaginative and prescient to review Titan’s environment, together with its fascinating climate patterns and gaseous composition, and in addition see by way of the haze to review albedo options (vibrant and darkish patches) on the floor. Titan’s environment is extremely fascinating, not solely attributable to its methane clouds and storms, but in addition due to what it will probably inform us about Titan’s previous and future—together with whether or not it at all times had an environment. We have been completely delighted with the preliminary outcomes.
“Staff member Sebastien Rodriguez from the Université Paris Cité was the primary to see the brand new pictures, and alerted the remainder of us by way of e mail: ‘What a wake-up this morning (Paris time)! Numerous alerts in my mailbox! I went on to my pc and began directly to obtain the info. At first look, it’s merely extraordinary! I feel we’re seeing a cloud!’
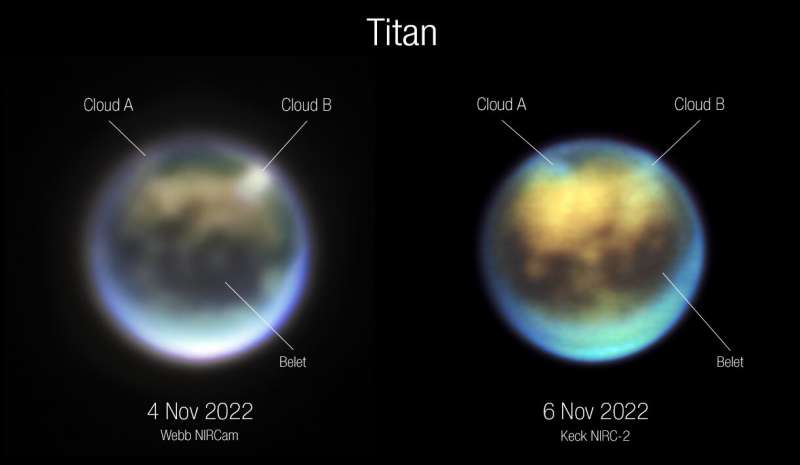
“Webb Photo voltaic System GTO Venture Lead Heidi Hammel, from the Affiliation of Universities for Analysis in Astronomy (AURA), had the same response: ‘Unbelievable! Love seeing the cloud and the plain albedo markings. So trying ahead to the spectra! Congrats, all!!! Thanks!’
“Thus started a day of frantic exercise. By evaluating totally different pictures captured by Webb’s Close to-Infrared Digicam (NIRCam), we quickly confirmed {that a} vibrant spot seen in Titan’s northern hemisphere was the truth is a big cloud. Not lengthy after, we seen a second cloud. Detecting clouds is thrilling as a result of it validates long-held predictions from pc fashions about Titan’s local weather, that clouds would kind readily within the mid-northern hemisphere throughout its late summertime when the floor is warmed by the sun.
“We then realized it was vital to search out out if the clouds have been shifting or altering form, which could reveal details about the air circulate in Titan’s environment. So we rapidly reached out to colleagues to request follow-up observations utilizing the Keck Observatory in Hawai’i that night.

“Our Webb Titan crew lead Conor Nixon from NASA’s Goddard Area Flight Heart wrote to Imke de Pater on the College of California, Berkeley, and Katherine de Kleer at Caltech, who’ve in depth expertise utilizing Keck: ‘We simply acquired our first pictures of Titan from Webb, taken final evening. Very thrilling! There seems to be a big cloud, we consider over the northern polar area close to Kraken Mare. We have been questioning a few fast response follow-up statement on Keck to see any evolution within the cloud?’
“After negotiations with the Keck workers and observers who had already been scheduled to make use of the telescope that night, Imke and Katherine rapidly queued up a set of observations. The purpose was to probe Titan from its stratosphere to floor, to attempt to catch the clouds we noticed with Webb. The observations have been successful! Imke de Pater commented: ‘We have been involved that the clouds could be gone once we checked out Titan two days later with Keck, however to our delight there have been clouds on the identical positions, trying like that they had modified in form.’
“After we received the Keck information, we turned to atmospheric modeling specialists to assist interpret it. A kind of specialists, Juan Lora at Yale College, remarked: ‘Thrilling certainly! I am glad we’re seeing this, since we have been predicting a superb little bit of cloud exercise for this season! We will not make sure the clouds on November 4 and 6 are the identical clouds, however they’re a affirmation of seasonal climate patterns.’
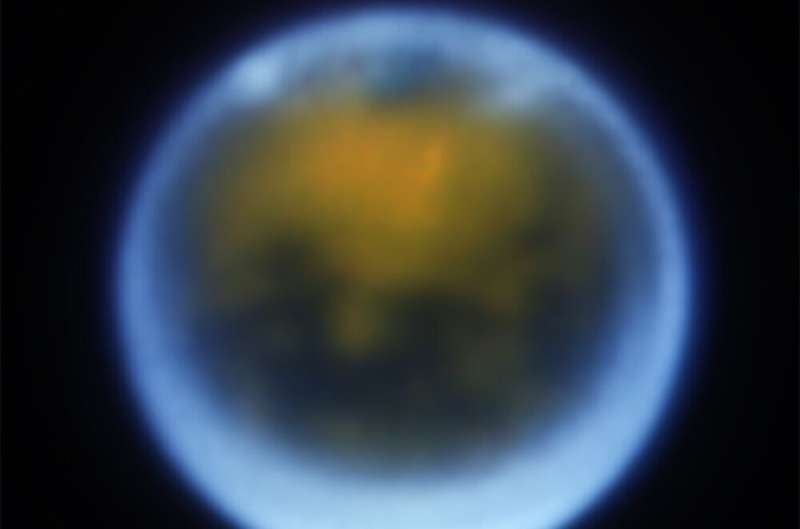
“The crew additionally collected spectra with Webb’s Close to-Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec), which is giving us entry to many wavelengths which might be blocked to ground-based telescopes like Keck by Earth’s environment. This information, which we’re nonetheless analyzing, will allow us to essentially probe the composition of Titan’s decrease environment and floor in ways in which even the Cassini spacecraft couldn’t, and to study extra about what’s inflicting the intense function seen over the south pole.
“We predict additional Titan information from NIRCam and NIRSpec in addition to our first information from Webb’s Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI) in Could or June of 2023. The MIRI information will reveal a fair better a part of Titan’s spectrum, together with some wavelengths we have now by no means seen earlier than. This may give us details about the complicated gases in Titan’s environment, in addition to essential clues to deciphering why Titan is the one moon within the solar system with a dense environment.
“Maël Es-Sayeh, a graduate pupil on the Université Paris Cité, is especially trying ahead to those observations: ‘I can be utilizing the info from Webb in my Ph.D. analysis, so it’s extremely thrilling to lastly get the actual information after years of simulations. I am unable to wait to see what is going to come partly two subsequent yr!'”
Offered by
Webb Area Telescope
Quotation:
Webb and Keck telescopes crew as much as monitor clouds on Saturn’s moon Titan (2022, December 1)
retrieved 1 December 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-12-webb-keck-telescopes-team-track.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.





